Securely And Efficiently Backup Data On Linux Or macOS With Vorta (BorgBackup GUI)
Vorta is a fairly new GUI for BorgBackup (or Borg for short), a command line backup tool with encryption, deduplication, compression and validation. Both Vorta and BorgBackup are free and open source software, and they run on Linux and macOS.
BorgBackup a secure, deduplicating backup program
BorgBackup is a secure and efficient command line backup tool that can store the data on any host available over SSH, or local drives.
- Secure. To protect the data, client-side 256-bit AES encryption is used, and data integrity and authenticity is verified using HMAC-SHA256.
- Efficient. Data deduplication is used for backups, only adding new data to the backup repository. This helps reduce both storage space usage and network bandwidth utilization, since it doesn't backup duplicate data blocks. The Borg deduplication does not depend on files and directory names staying the same, complete files or time-stamps staying the same, or the absolute position of a data chunk inside a file. Compression is also supported - using lz4, zstd, zlib or lzma.
What's more, Borg can mount backup snapshots as userspace filesystems, so you can take a look at the contents of a backup before restoring it, or restore only some file, using a regular file manager.
For how to install BorgBackup, head over to its installation page (hint: it's most probably available in your Linux distributions' repositories - this includes Arch Linux, Debian / Ubuntu / Linux Mint, Gentoo, Fedora, openSUSE, and Raspbian.).
Vorta Backup Client (BorgBackup GUI)
 |
| Vorta application window, its system tray menu, and a backup mounted and opened in Nautilus file manager |
Vorta is a graphical user interface for BorgBackup that runs on macOS and Linux. Its features include:
- Backup profiles. These can be used to backup different sources to different destinations, using the same SSH keys. For example, this allows backing up some important files to a remote server, while doing a full backup to a local storage device.
- Backup scheduling with a log viewer, and custom shell commands that can run pre or post backup.
- Backup archives view with timestamps, from where you can extract, mount, check, delete or prune backups.
- Configurable pruning (remove old backups after a certain period).
- Built-in SSH key generation.
- Filenames/path exclude patterns.
- GUI options like dark/light system tray icon, light/dark application theme, display notifications when backups fail and/or are successful, and automatically start Vorta at login.
How to install Vorta BorgBackup GUI
To download Vorta for macOS, head over to its releases page. For Linux you'll find the binary posted here.
On Linux, Vorta is now available on Flathub, as a flatpak package, so it's easier to install and update on any Linux distribution.
For Arch Linux / Manjaro, install Vorta from AUR.
Debian 11+, Ubuntu 21.04+ (and Pop_OS 21.04), etc., can install Vorta from the official repositories, using:
sudo apt install vortaSolus OS users can install Vorta from the repos:
sudo eopkg it vortaOn Fedora, Vorta is available in a Copr third-party repository, and it can be installed using the following commands:
sudo dnf copr enable luminoso/vortasudo dnf install vortaVorta starts hidden, running in the system tray. If you use Gnome Shell, you may want to install the AppIndicator support extension to access the Vorta system tray menu (not required on Ubuntu since this extension is installed by default). If the Vorta tray icon doesn't match your panel color (it uses a dark tray icon by default that can be hard to see if you're using a dark panel), change it to a light icon from the Vorta settings (on the Misc tab).
You may also launch the Vorta GUI and open its main window:
vorta -fAlternatively, you may also install Vorta from source, using PIP.
Getting started with Vorta
Step 1. Setup a SSH key.
To get started with Vorta, launch the application and on the Repository tab, next to SSH Key, click the drop-down and select
Create new key. Leave the recommended defaults unless you want some different settings and you know what you're doing, and press the Generate and copy to clipboard button. Close the Vorta SSH Key generation window once the key has been generated.If you don't want Vorta to ask for the SSH password each time you create a new backup, you'll want to create a SSH passwordless login. That's beyond the point of this article, but you can find guide for this online, and it's quite easy.
This SSH key generation step is only required if you want to use a remote backup repository. If you're using Vorta to backup to a local storage device you can skip this step.
It's worth noting that when using a remote repository for backups, BorgBackup needs to be installed on the remote server. Check out the BorgBackup installation page for details.
Step 2. Create a new backup repository.
Next, you should see a
Repository field with a drop-down. Click Select Backup Destination -> Initialize New Repository and:- press on the folder icon if you want to store the backup locally, and select the backup directory.
- enter the repository URL if backing up to a remote server, and for the
SSH Keymake sure you select the same SSH key created in the previous step.
Enter a password and press
Add to initialize the new backup repository.Step 3. Select the files and folders to back up.
On the
Sources tab in Vorta, press Add Folder and/or Add File to add the files and folders you want to back up. You may exclude some files/folders or add exclude patterns here.Step 4. Create a backup using Vorta.
Now it's time to create your first backup using Vorta and BorgBackup. Press
Start Backup in the lower left-hand side corner of the Vorta window to create a backup. All backups can be seen on the Archives tab:You may also want to create an automatic backup schedule:
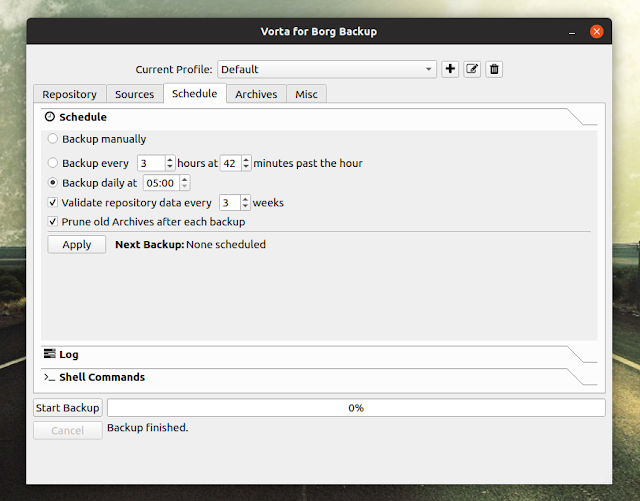
This can be done from the
Schedule tab. Select the time interval for your backups, optionally enable pruning of old archives, and press Apply.Want to restore a backup created using Vorta? Go to the Vorta
Archives tab, select a snapshot and press the Extract button. You can also mount a backup by selecting it and pressing Mount - this way you can open it using your file manager and check the backup contents, copy some files from the backup without restoring it, etc.